Osteopathy General Introduction
What is Osteopathy?
Osteopathy is an alternative medicine that focuses on the physical manipulation of muscles and bones to treat various health conditions. Practitioners believe in the body's natural ability to heal itself, concentrating on the musculoskeletal system as a key component of overall health.

Osteopathic Philosophy
The philosophy of osteopathy is based on several core principles:
-
Holistic Approach
Osteopathy sees the body as a unified whole, emphasizing the interconnectedness of its systems and the importance of considering the whole person in diagnosis and treatment.
-
Structure and Function
Osteopathy believes the body's structure (bones, muscles, and tissues) is closely related to its function (movement, circulation, nerve impulses). Practitioners focus on optimizing the musculoskeletal system to enhance overall health.
-
Self-Healing
Osteopathy recognizes the body's innate ability to heal itself. Treatment aims to facilitate this natural process by removing obstacles, restoring balance, and supporting the body's mechanisms.
-
Manipulative Therapy
A hallmark of osteopathy is the use of hands-on techniques, such as osteopathic manipulative treatment, to diagnose and treat musculoskeletal problems. These techniques aim to improve joint mobility, relieve muscle tension, enhance circulation, and promote overall function.
-
Preventive Care
Osteopathy emphasizes preventive care and health maintenance. By addressing underlying musculoskeletal issues and promoting healthy lifestyle habits, practitioners aim to prevent illness and injury.
-
Patient-Centered Care
Osteopathy emphasizes understanding each patient's unique circumstances, including physical, emotional, and social factors. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual, considering their specific needs and goals.
Osteopathy combines respect for the body's natural abilities with hands-on therapeutic techniques to promote health and well-being. It offers a holistic approach to healthcare that complements conventional medical practices.
Osteopathy History

Osteopathy Treatments
Osteopathy is a form of alternative medicine that emphasizes the physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones. Osteopathic practitioners are focus on holistic treatment and the interrelationship between the body's structure and function. Here are some of the areas commonly addressed by osteopathy:
Musculoskeletal System
-
Back Pain
Including lower back pain and sciatica.
-
Neck Pain
Conditions like whiplash or chronic neck pain.
-
Joint Pain
Such as arthritis, bursitis, and sports injuries.
-
Muscle Pain
Including conditions like muscle strains and sprains.
Nervous System
-
Headaches and Migraines
Often related to tension or structural issues.
-
Nerve Pain
Such as carpal tunnel syndrome or radiculopathy.
Circulatory System
-
Circulatory Problems
Including issues related to poor blood flow.
-
Lymphatic Drainage
Helping to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic function.
Respiratory System
-
Asthma
Helping to improve breathing mechanics.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Assisting with breathing and posture.
Digestive System
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Alleviating symptoms through manipulation techniques.
-
Constipation
Improving digestive function through abdominal massage and other techniques.
General Health and Well-being
-
Postural Problems
Correcting posture to alleviate pain and prevent future issues.
-
Stress and Tension
Reducing overall body tension and improving relaxation.
Pediatric Care
-
Colic and Sleep Issues in Infants
Gentle techniques to soothe and improve sleep.
-
Developmental Issues
Helping with alignment and growth-related problems.
Women’s Health
-
Pregnancy-related Issues
Managing back pain and other discomforts during pregnancy.
-
Postpartum Care
Assisting recovery after childbirth.
Elderly Care
-
Mobility Issues
Improving movement and reducing pain in older adults.
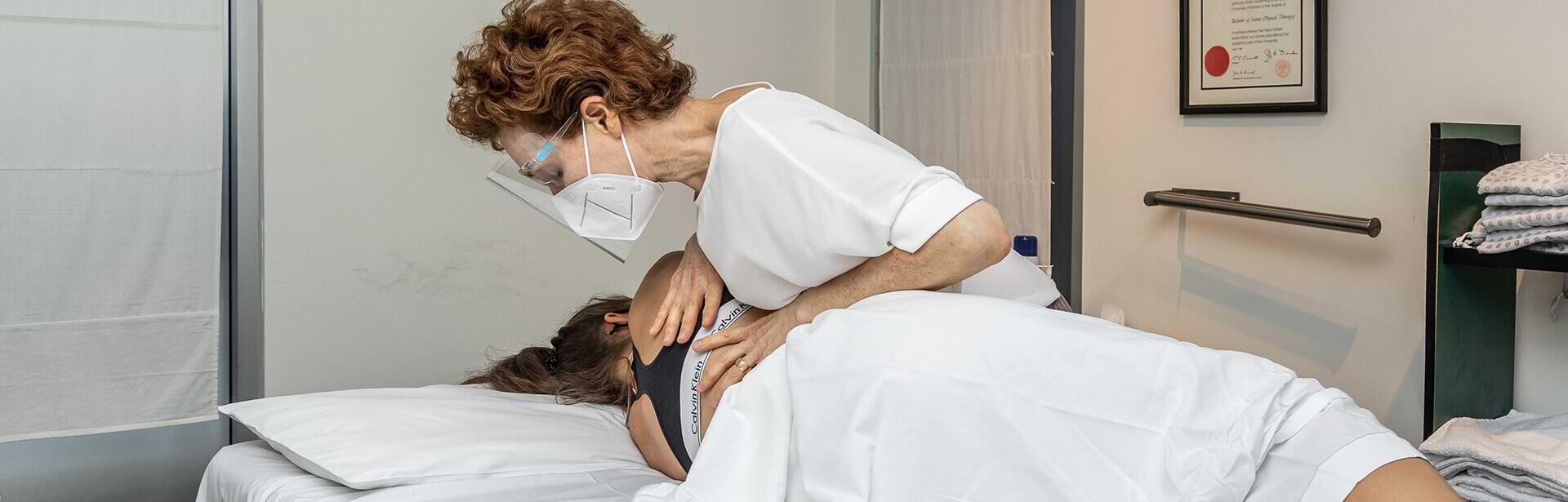
Chronic Conditions
Osteopaths use various techniques, including stretching, massage, and manipulation of the spine and joints, to improve health and well-being. They aim to enhance the body's self-healing mechanisms and ensure all body systems work harmoniously and managing long-term conditions like osteoarthritis..
Cranial-Sacral Therapy
Cranial-sacral therapy, also known as cranial osteopathy, focuses on the cranial-sacral system, which includes the membranes and cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
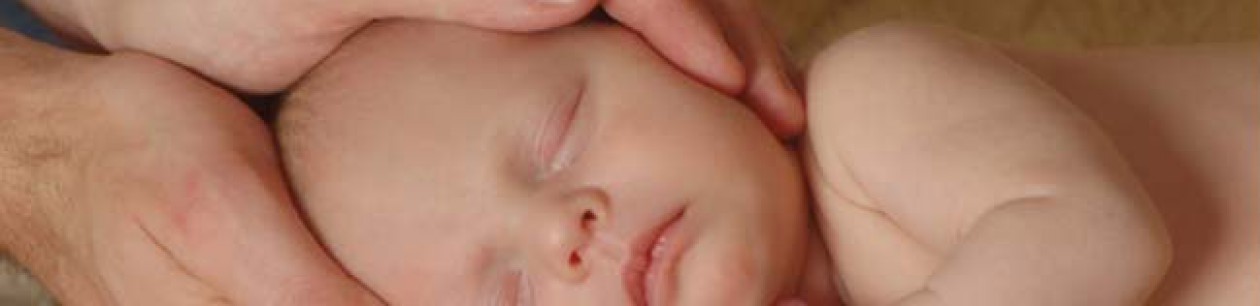
Key Aspects of Cranial-Sacral Therapy
-
Philosophy
Based on the idea that subtle movements of the cranial bones and sacrum can be detected and manipulated to enhance the body's self-healing abilities.
-
Techniques
Therapists use gentle, non-invasive touch to assess and manipulate the cranial bones, sacrum, and other parts of the body.
-
Conditions Treated
Used for headaches, migraines, neck and back pain, stress-related disorders, TMJ dysfunction, and other musculoskeletal or neurological issues. It is also applied in pediatric care for conditions like colic, development al delays, and feeding difficulties.
-
Integration with Osteopathy
While focused on the cranial-sacral system, it is integrated into broader osteopathic practice. The practitioner specialized in cranial-sacral therapy may use it as part of a holistic treatment plan.
-
Evidence and Research
The efficacy of cranial-sacral therapy is a topic of ongoing research and debate. Some studies suggest potential benefits, but more research is needed to establish its effectiveness definitively.
Areas Addressed by Osteopathy
-
Lymphatic System
Techniques to support lymphatic drainage and circulation, enhancing immune function, reducing swelling, and aiding detoxification.
-
Spine
Techniques restore spinal alignment, reduce muscle tension, and improve nerve function, alleviating back pain and enhancing mobility.
-
Colon
Addressing functional issues like constipation or IBS, improving digestive function, and relieving discomfort through musculoskeletal balance and abdominal relaxation.
In osteopathy, each patient is treated as a whole person, considering musculoskeletal health, organ function, and overall well-being. Each practitioner uses various manual techniques and provides guidance on lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management to support optimal health outcomes. Osteopathy often complements conventional medical treatment, especially for musculoskeletal conditions and functional health issues.